Updated: Jun 22, 2023 By: Dessign Team
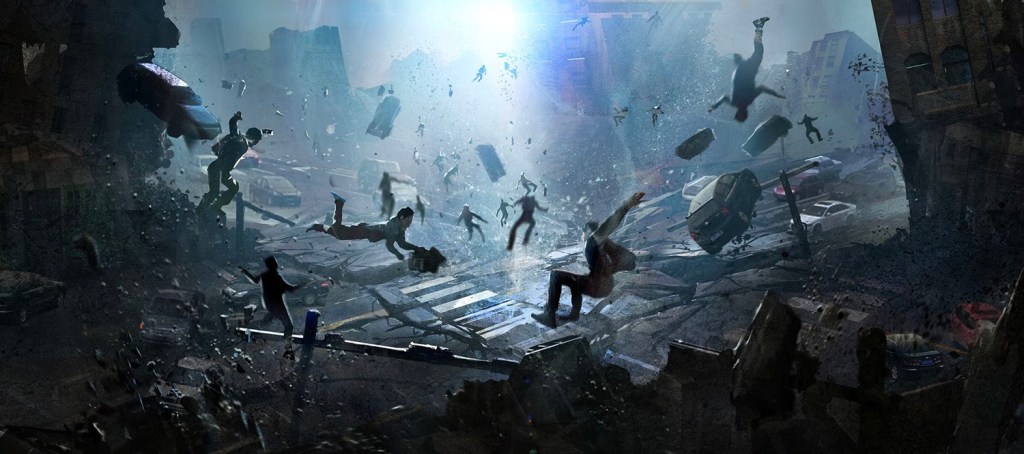

In the world of visual media, animation has become an increasingly popular and influential form of storytelling. Among its various techniques, 3D animation stands out as a dynamic and visually captivating method that has transformed the entertainment, advertising, and gaming industries.
This article explores the fascinating world of 3D animation software, including its types, processes, and diverse range of applications.
Understanding 3D Animation:
Definition and Concept:
3D animation refers to the creation of moving images using three-dimensional computer graphics. Unlike traditional 2D animation, which relies on hand-drawn frames, 3D animation employs computer-generated imagery (CGI) to produce realistic and immersive visuals.
It involves modeling, texturing, rigging, animating, drawing, and rendering objects and characters within a virtual three-dimensional space.
Advantages of 3D Animation:
The utilization of 3D animation brings numerous advantages, including enhanced realism, depth, and visual effects. It enables animators to create lifelike characters, intricate environments, and breathtaking special effects.
The flexibility and versatility of 3D animation allow for creative expression and seamless integration with other media formats.
Types of 3D Animation
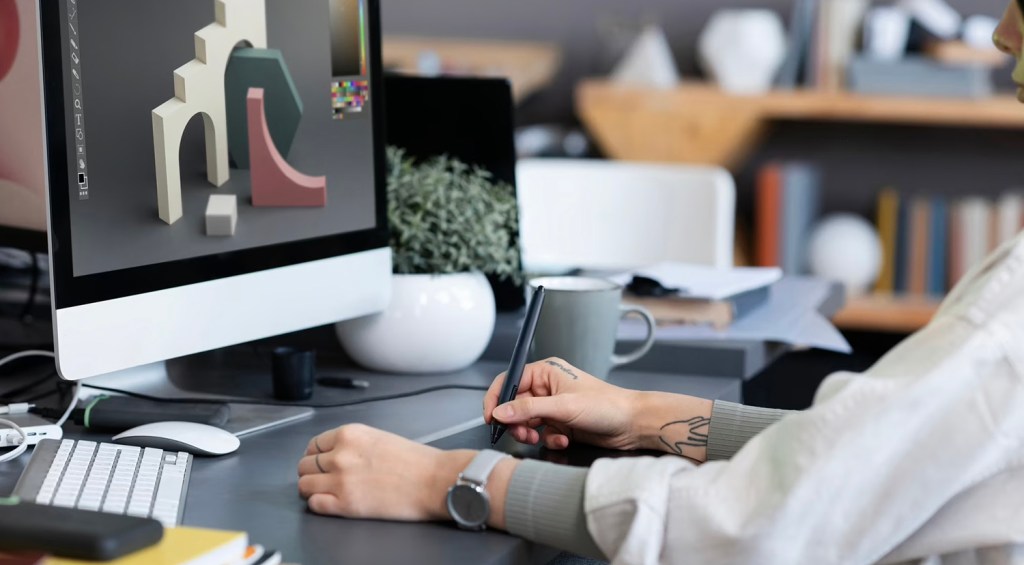

Character Animation:
Character animation focuses on bringing virtual characters to life. Through the process of rigging and animating, artists create movements, expressions, and interactions that convey emotions and personalities. Character animation finds extensive application in films, video games, and advertisements.
Motion Graphics:
Motion graphics involve animating graphical elements such as typography, shapes, and logos to communicate information, evoke emotions, or enhance storytelling. This type of 3D animation is frequently utilized in title sequences, promotional videos, and user interfaces.
Architectural and Product Visualization:
3D animation plays a significant role in architectural and product visualization by allowing designers to present their creations in a realistic and immersive manner. By creating virtual models, animators can showcase architectural designs, interior spaces, and product prototypes, aiding in marketing and client presentations.
Visual Effects (VFX):
VFX are computer-generated imagery used to enhance or create elements that cannot be achieved practically. 3D animation is integral to VFX, enabling the creation of fantastical creatures, explosive environments, and breathtaking sequences. It finds extensive use in the film and television industry.
Ways to use 3D animation

The popularity of 3D animation is on the rise, offering countless ways to utilize its power. It can be used in entertainment, advertising, gaming, architecture, training, and virtual reality experiences.
The potential of 3D animation is vast and can be used to create visually engaging and compelling ads, lifelike graphics in video games, realistic visualizations of buildings, and immersive worlds in virtual reality.
One notable example that showcases its capabilities is 1995's “Toy Story” by Pixar Animation Studios – the first full-length feature entirely made using CGI. It revolutionized the world of animation and has had a lasting influence in the entertainment industry.
Creating 3D animation is like running a marathon. Except, instead of sweating, you're stressing if your computer will crash.
3D animation process

Creating 3D animation is an intricate process which brings virtual characters and worlds to life. To produce a high-quality output, many steps are needed – from concept to final rendering. These include modeling, rigging, texturing, animating, lighting, and rendering – each needing careful attention and artistic skill.
A look at the 3D animation process:
| Modeling | Making digital 3D models of characters, objects, and environments using specialized software. |
| Rigging | Adding a virtual skeleton with controls for flexible movement of characters or objects. |
| Texturing | Giving models a realistic look by applying materials and textures. |
| Animating | Creating movement using keyframe animation or motion capture techniques. |
| Lighting | Setting up virtual lights and adjusting properties to create atmosphere and effects. |
| Rendering | Processing the final frames of the 3D animation, taking into account lighting, shadows, reflections, and other visuals. |
Each stage needs specialized software and tech knowledge. Also, it takes several professionals, such as modelers, riggers, texture artists, animators, and lighting specialists, to make a cohesive result.
3D animation has changed industries like film, gaming, advertising, and architecture. It allows us to make realistic and immersive virtual environments, unlocking creative and storytelling possibilities.
An example of this is a breathtaking sequence in a blockbuster movie. This involved designing and animating intricate characters and environments, bringing the audience into a fantastical world. It took dedication, detail, and technical skill to make this, showing the power of 3D animation.
Differences between 2D and 3D animation

Distinguishing between 2D and 3D animation is based on how visuals are created. 2D animation involves characters and objects created on a flat surface, while 3D animation allows for depth and varied viewing angles.
| 2D Animation | 3D Animation |
|---|---|
Flat visuals Height & width only Less realistic look Hand-drawn approach | Visually 3D with depth Can rotate & view from different angles More realistic appearance Digital creation via computer software |
3D animation stands out as it can create lifelike characters & environments via digital models. This gives a level of realism that 2D animation cannot.
The growing demand for 3D content has spurred technology & software development, which helps animators craft intricate & immersive experiences.
Fun fact: The Pixar movie “Toy Story” (1995) was the first full-length feature film made entirely with CGI techniques.
Unlock your imagination with 3D animation – it's the only art form where you can get characters to wow the audience without risking any broken bones (unless you're a time-pressed animator)!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is 3D animation?
A: 3D animation is a type of computer animation that involves creating three-dimensional models and characters to simulate movement and motion.
Q: How is 3D animation different from 2D animation?
A: 3D animation is created using three-dimensional models that can be viewed from any angle in virtual space, while 2D animation is a flat, two-dimensional image that is viewed on a screen.
Q: What software is used for 3D animation?
A: There are many software programs used for 3D animation, including Maya, Blender, 3ds Max, and Cinema 4D.
Q: What industries use 3D animation?
A: 3D animation is used in many industries, including film and television production, video game development, architecture, interior design, medical simulations, and product visualization.
Q: Are there any specific skills required to create 3D animation?
A: Yes, 3D animators need to have a strong understanding of computer graphics and programming, as well as knowledge of modeling, texturing, lighting, and rendering techniques.
Q: How long does it take to create a 3D animation?
A: The amount of time it takes to create a 3D animation can vary depending on the complexity of the project, but it can range from several weeks to several months.